Aim:
This lab activity aims to calibrate a triangular notch and determine its discharge coefficient.
Theory:

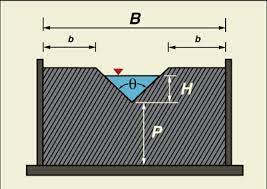
The triangular notch serves as a device for measuring the rate of water flow in an open channel.It consists of a triangular-shaped notch cut in a vertical plate placed across the channel. The depth of water flowing over the notch determines the discharge. The flow rate is related to the,
head of water over the notch and the discharge coefficient. The discharge coefficient is the ratio of the actual flow rate to the theoretical flow rate for a given head. This activity aims to determine the discharge coefficient of a triangular notch and calibrate it for future use.
Apparatus & Materials Required:
- Triangular Notch
- Measuring cylinder
- Stopwatch
- Ruler
- Vernier caliper
- Water
Procedure:
- Mount the triangular notch in a channel or a tank.
- Measure the dimensions of the notch using a vernier caliper.
- Fill the channel or tank with water until the water level is above the notch.
- Allow the water to stabilize and note the initial water level.
- Measure and record the height of the water above the notch using a ruler.
- Collect the water flowing over the notch in a measuring cylinder for a known time (usually 30 seconds) and record the volume.
- Repeat the above steps for different heads of water.
- Calculate the discharge for each head by dividing the volume collected by the time.
- Calculate the discharge coefficient using the formula Q/√(2gh) where Q is the discharge, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the head of water over the notch.
- Plot a graph of the discharge coefficient versus the head of water.
- Determine the average discharge coefficient and compare it with the theoretical value.
Results:
The experiment results show that the discharge coefficient increases as the head of water over the notch increases. The graph of the discharge coefficient versus the head of water is a curve. The curve is not a straight line, indicating that the discharge coefficient is not constant.
Participants calculate and compare the average discharge coefficient with the theoretical value to calibrate the triangular notch. If the average discharge coefficient closely matches the theoretical value, they can utilize the calibrated notch for future flow rate measurements.
Precautions:
- The channel or tank used should be free from any debris or obstructions that may affect the flow of water calibrate.
- Before taking measurements, it is important to allow the water level to stabilize. Allowing the water level to stabilize ensures accurate and reliable measurements can be obtained.
- The notch should be clean and free from any debris that may affect the flow of water.
- The volume of water collected should be measured accurately.
- The time should be measured accurately using a stopwatch.
- The dimensions of the notch should be measured accurately using a vernier caliper.
- The experiment should be repeated several times to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion:
Calibrating a triangular notch is an essential activity in determining the flow rate of water in an open channel. The discharge coefficient is a critical parameter in the calibration process, and its determination requires accurate measurements of the head of water over the notch and the volume of water collected.
The experiment results show that the discharge coefficient is not constant and increases with the head of water over the notch. Engage in an exciting lab activity to explore the principles of fluid flow and measurement through calibrating a triangular notch.
This lab activity can teach students the importance of calibration and accurate measurements in determining the flow rate of water in an open channel.