Aim:
This lab activity aims to calibrate a rectangular notch and determine the discharge coefficient of the notch using theoretical and experimental Calibrating methods.
Theory: of calibrating

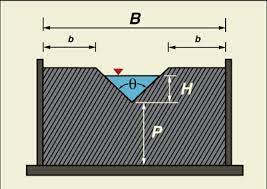
The rectangular notch serves as a widely employed device for measuring water flow rate in open channels. It consists of a rectangular opening in a vertical wall with a sharp upstream,
edge and a downstream edge that is usually sloped at an angle of 60 degrees.
When water flows through the notch, it forms a well-defined, sharp-edged weir over the downstream edge, and the height of the water above the bottom of the gap is proportional to the flow rate.
The discharge coefficient, which defines the efficiency of the notch, is the ratio of the actual discharge through the notch to the theoretical discharge based on a specific criterion.
the notch geometry and the head of water above the bottom of the notch.
Apparatus & Materials Required:
The following apparatus and materials are required for this lab activity:
- Rectangular Notch
- Water tank
- Measuring cylinder
- Stopwatch
- Vernier Calipers
Procedure: calibrating
- Measure the dimensions of the rectangular notch using vernier calipers.
- Fill the water tank with water to a sufficient height.
- Place the rectangular notch at the outlet of the water tank.
- Measure the head of water above the bottom of the notch using the measuring cylinder.
- Start the stopwatch and record when a known volume of water passes through the gap.
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 for different values of the head of water.
- Tabulate the data obtained and calculate the discharge coefficient for each value of the head of water.
- Plot a graph of the discharge coefficient against the head of water.
- Compare the experimental results with the theoretical values of the discharge coefficient.
Results:
The experiment involved measuring the flow rate of water through a rectangular notch using different head heights.
We recorded the time taken, using a stopwatch, for a known volume of water to pass through the notch.
We tabulated the data and performed calculations to determine the discharge coefficient for each value of the head of water.
Us plotted the values of the discharge coefficient on a graph against the head of water to observe the variation calibrating.
You can utilize the experiment results to calibrate the rectangular notch, enabling accurate calibration and measurement.
for accurate flow rate measurement in various applications such as irrigation, water supply, and hydrology.
Precautions: calibrating
- Ensure the rectangular notch is clean and free from any obstruction before use.
- Please make sure to fill the water tank to a sufficient height and maintain a constant water level throughout the experiment.
- Ensure that the stopwatch is started and stopped precisely.
- Ensure that the measuring cylinder is accurate and calibrated.
Conclusion:
The calibration of a rectangular notch is an important activity for determining the discharge coefficient of the notch. The theoretical and experimental methods used in this lab activity provide an understanding of the efficiency of the notch in measuring the flow rate of water in open channels.
The results from this lab activity provide valuable data for calibrating the notch to ensure accurate flow rate measurement in various applications, including irrigation, water supply, and hydrology.